Kalor Untuk Perubahan Wujud
A. Mencair
Mencair adalah perubahan wujud zat dari padat menjadi cair
$$\bbox[yellow, 5px, border: 2px solid red] {Q = m_{\text{es}} \cdot L_{\text{es}}}$$
\(m_{\text{es}} = \text{ massa es yang mencair}\)
\(L_{\text{es}} = \text{ kalor lebur es } = 336.000 \text{ J/kg atau } 80 \text{ kal/g}\)
B. Menguap
Menguap adalah perubahan wujud zat dari cair menjadi uap
$$\bbox[yellow, 5px, border: 2px solid red] {Q = m_{\text{u}} \cdot L_{\text{uap}}}$$
\(m_{\text{u}} = \text{ massa air yang menguap}\)
\(L_{\text{uap}} = \text{ kalor uap air } = 2.260.000 \text{ J/kg atau } 540\text{ kal/g}\)
Kalor Untuk Perubahan Suhu
$$\bbox[yellow, 5px, border: 2px solid red] {Q = m \cdot c \cdot \triangle T}$$
atau
$$\bbox[yellow, 5px, border: 2px solid red] {Q = C \cdot \triangle T}$$
keterangan:
\(Q = \text{ kalor yang dibutuhkan (J)}\)
\(m = \text{ massa zat (kg)}\)
\(c = \text{ kalor jenis zat }\) (J/kg °C)
Kalor jenis air = 4.200 J/kg °C atau 1 kal/g °C
Kalor jenis es = 2.100 J/kg °C atau 0,5 kal/g °C
\(C = \text{ kapasitas kalor} (\text{J} \cdot ^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1})\)
Grafik perubahan suhu dan perubahan wujud zat
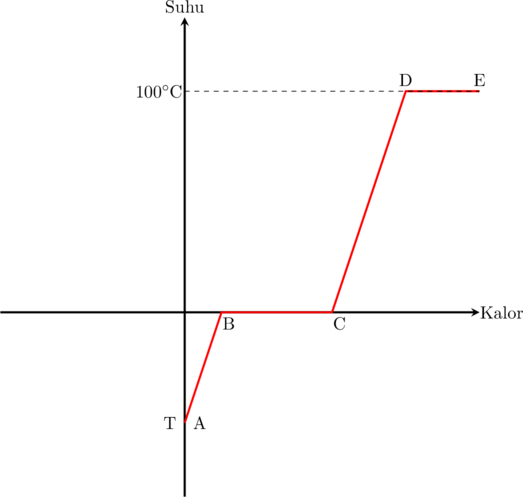
Keterangan:
A − B : kenaikan suhu es
B − C : perubahan wujud es menjadi air
C − D : kenaikan suhu air
D − E : perubahan wujud air menjadi uap
